Rotator Cuff
September 2020
What is the Rotator Cuff, and How Does It Get Injured?
by Jesse Morse-Brady, FNP-BC
The shoulder is a complex joint, which can move in many directions. The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and tendons that contribute to shoulder motion. These four muscles and tendons are called the supraspinatous, infraspinatous, subscapularis, and teres minor (see illustration, below).
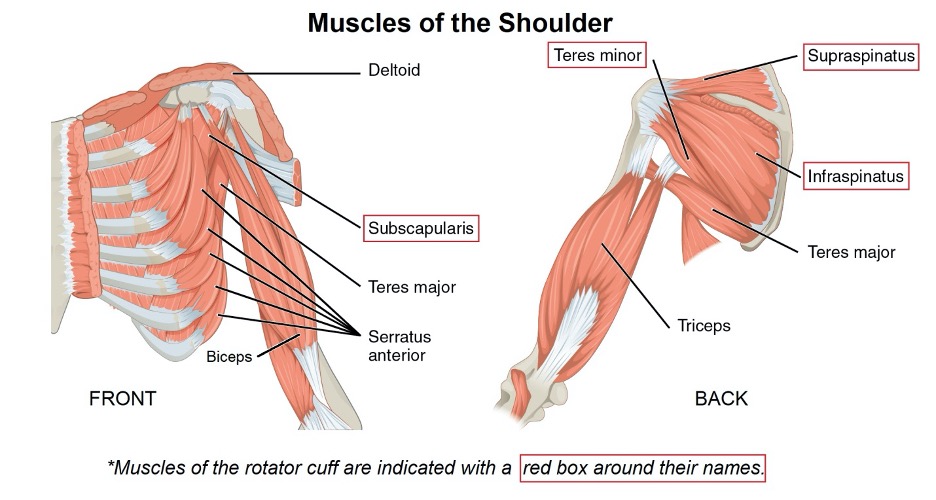
Rotator Cuff Injuries
Injuries to the rotator cuff are often referred to as “rotator cuff tears.” This phrase refers to damage to or tearing of one or more of the muscles or tendons that make up the rotator cuff. Damage to the rotator cuff structures can occur with a sudden injury, such as falling on the shoulder or lifting/pulling a heavy object. The rotator cuff can also sustain gradual damage over time, in which the muscles and tendons slowly wear down through a number of small injuries. When gradual damage to these structures occur, a person can develop sudden shoulder pain or decreased movement without having a traumatic injury.
Regardless of the manner in which the rotator cuff muscles or tendons become injured, the most frequent symptoms include shoulder pain and decreased movement of the shoulder, such as being unable to lift the injured arm above the shoulder or being unable to reach behind the back. There are also many other causes of shoulder pain, which do not involve the rotator cuff. Orthopaedic providers can distinguish rotator cuff injuries from other causes of shoulder pain through specific examinations and diagnostic images.
Treatment of Rotator Cuff Injuries
There are several different ways that rotator cuff injuries can be treated, which may include the following:
- Rest and activity modification
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy
- Surgical repair
Rotator cuff injuries that do not cause severe discomfort or significantly limit motion can often be treated without surgery, whereas injuries that cause persistent pain or activity limitation may benefit from surgical repair.
Treatment planning is individualized for each patient, based on the type of injury, personal preferences, and treatment goals. The Fremont Orthopaedics team offers specialty care for shoulder concerns, including rotator cuff injuries. For any additional questions or to schedule an appointment with one of our providers, call (307) 332-9720.
This document contains general guidelines and is not a substitute to your provider’s instructions or an alternative to seeking appropriate medical care or follow-up appointments. For questions or concerns, seek professional medical attention. For medical emergencies, call 911.